Since this article was published in 2009 there have been several significant advancements to Youtube and web 2.0 in general, to the point where several of the points made in Urrichio’s piece seem quaint and antiquated.
Youtube specifically has become a media giant, and is now unquestionably a separate entity from the traditional media that it was only a companion to six years ago. Content creators such as PewDiePie have made careers out of creating videos for the website. The Swedish gamer in particular raked in $7.4 million last year largely due to advertising revenue from his videos.
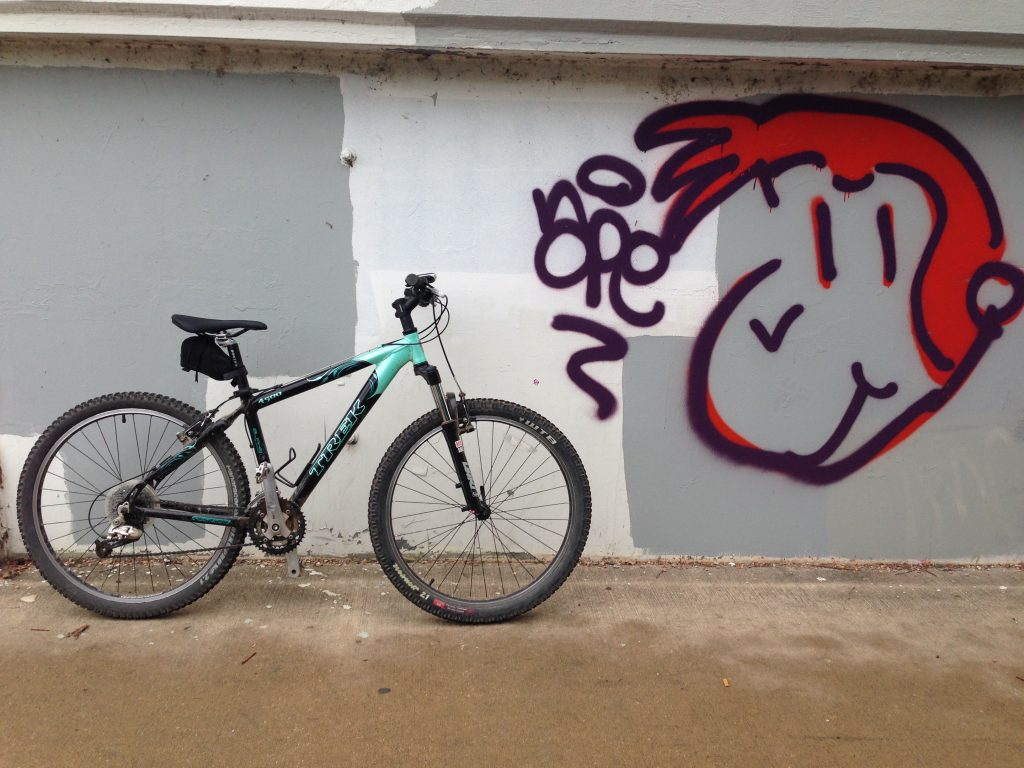
The trademark of Web 2.0 has been individual content creators gaining notoriety through uploading their own content. This is on the surface a very democratic approach, and if you create quality content you will be recognized and celebrated for it. In practice, the barrier for entry is still very high, and most of the well-known Youtube celebrities use very expensive recording and audio equipment. Tech reviewer MKBHD, for example, uses a $50,000 RED video camera to record his videos. Popular vlogger Casey Neistat uses his previous experience in advertising to create videos with cinematography that would be impossible for a novice to create. This influx of money and experience to the Youtube scene is a far cry from the early days of the site when videos such as Charlie bit my finger were all the rage
.
Still, even with this influx of money and experience to web 2.0, it still operates around the principle of individual creation. I believe that this will change with the advent of Web 3.0, and I think that we have begun to see the start of Web 3.0 already. Web 3.0 will likely be defined as the introduction of corporations into the web, who create their own content and charge for it. The most obvious Web 3.0 candidate right now would be Netflix, which charges for access to their catalogue of movies and shows, which include their own television shows published on the service.
Other companies are starting to experiment with broadcasting their content on the web first. VICE media has deals with Snapchat, Go90, and Apple Music to produce exclusive series and publishes their flagship television series on HBO, which has recently developed HBO Now, a Netflix clone that publishes HBO’s series at the same time that they come on TV.
Even sports, traditionally a stalwart of cable TV, has begun to move to the web. The NFL reached a deal with Twitter today to broadcast its Thursday Night Football games on the app. The ability to stream NFL games without a cable subscription, which this deal will likely entail, will be groundbreaking for the web.